|
|
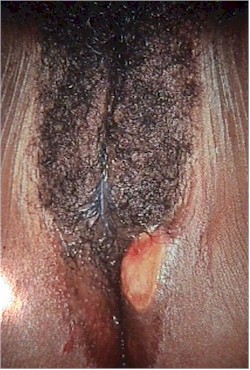
Primary Syphilis
The distinguishing symptom is a painless ulcer on the vulva, vagina or cervix. The ulcer is non-tender, has a well-defined border and smooth base. It starts as a macular lesion, forms a central papule, then erodes to form an ulcer crater. Regional lymph nodes are enlarged, firm, mobile, and painless.
The diagnosis is confirmed by darkfield examination of serous fluid from crater (looking for spirochetes), a VDRL or RPR test.
Watch for the Herxheimer reaction beginning within a few hours of treatment, with fever, chills, malaise, headache and myalgia. It is treated with bedrest and aspirin and will disappear within 24 hours. Continue treatment.
Optimal treatment is:
- Benzathine penicillin G 2.4 million units IM in a single dose
but for those allergic to penicillin, you may substitute:
- Doxycycline 100 mg orally twice a day for 2 weeks, or
- Tetracycline 500 mg orally four times a day for 2 weeks.
If the patient is pregnant, tetracyclines should not be used. Should the pregnant patient also be allergic to penicillin, desensitization is recommended by many, but operational circumstances may not allow for that. In such cases erythromycin or Azithromycin can be effective, although the optimal dosage is unknown. The main concern here is that if insufficient antibiotic gets across the placenta and to the fetus, fetal syphilis will be insufficiently treated.
Bureau of Medicine and
Surgery |
Operational Obstetrics
& Gynecology - 2nd Edition |