|
|
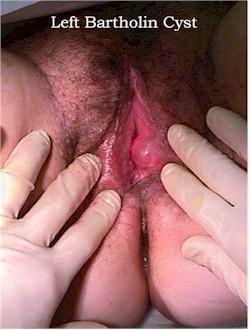
Bartholin Cyst and Abscess
The Bartholin glands are located on each side of the vaginal opening at the level of the posterior fourchette. Normally, they are neither visible nor palpable.
Bartholin cysts are painless swellings in the labia majora. They are not infected and can be safely watched. They may occur following trauma or infection, but many are essentially spontaneous. It is a relatively simple procedure to drain them, but in operational settings, there is little need to do that as they are generally without symptoms.
When infected (Bartholin abscess), the labia majora becomes excruciatingly painful. Some of these will drain spontaneously within 72 hours. This process may be hastened by warm moist dressings or sitz baths.
Incision and Drainage of the abscess gives immediate relief. Watch a video for a demonstration of this procedure on a Bartholin cyst:
- Give local anesthetic of 1% Xylocaine over the incision site (thin area of skin medial to the cyst).
- Steady the cyst or abscess with one hand while a scalpel is directed into the center of the abscess.
- Purulent drainage should be cultured for gonorrhea.
- Antibiotic therapy is optional but wise, particularly if the patient is febrile, the abscess large, or the skin is red or tender.
Recurrent Bartholin abscesses are common and these may need surgical removal, marsupialization, or insertion of a Word Catheter. These are best handled by a gynecologic surgeon. In an isolated military setting, a simple incision and drainage procedure will always be temporarily effective and is a reasonable choice.
Bureau of Medicine and
Surgery |
Operational Obstetrics
& Gynecology - 2nd Edition |